The filenames now represent composite ids (stream id + recording id) rather
than a separate uuid system with its own reservation for a few benefits:
* This provides more information when there are inconsistencies.
* This avoids the need for managing the reservations during recording. I
expect this to simplify delaying flushing of newly written sample files.
Now the directory has to be scanned at startup for files that never got
written to the database, but that's acceptably fast even with millions of
files.
* Less information to keep in memory and in the recording_playback table.
I'd considered using one directory per stream, which might help if the
filesystem has trouble coping with huge directories. But that would mean each
dir has to be fsync()ed separately (more latency and/or more multithreading).
So I'll stick with this until I see concrete evidence of a problem that would
solve.
Test coverage of the error conditions is poor. I plan to do some restructuring
of the db/dir code, hopefully making steps toward testability along the way.
Introduction
Moonfire NVR is an open-source security camera network video recorder, started
by Scott Lamb <slamb@slamb.org>. It saves H.264-over-RTSP streams from
IP cameras to disk into a hybrid format: video frames in a directory on
spinning disk, other data in a SQLite3 database on flash. It can construct
.mp4 files for arbitrary time ranges on-the-fly. It does not decode,
analyze, or re-encode video frames, so it requires little CPU. It handles six
1080p/30fps streams on a Raspberry Pi
2, using
less than 10% of the machine's total CPU.
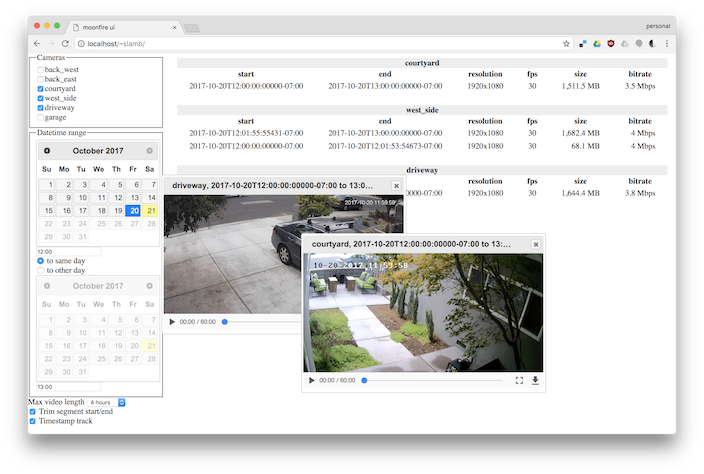
So far, the web interface is basic: a filterable list of video segments, with support for trimming them to arbitrary time ranges. No scrub bar yet. There's also no support for motion detection, no authentication, and no config UI.
This is version 0.1, the initial release. Until version 1.0, there will be no compatibility guarantees: configuration and storage formats may change from version to version. There is an upgrade procedure but it is not for the faint of heart.
I hope to add features such as salient motion detection. It's way too early to make promises, but it seems possible to build a full-featured hobbyist-oriented multi-camera NVR that requires nothing but a cheap machine with a big hard drive. I welcome help; see Getting help and getting involved below. There are many exciting techniques we could use to make this possible:
- avoiding CPU-intensive H.264 encoding in favor of simply continuing to use the camera's already-encoded video streams. Cheap IP cameras these days provide pre-encoded H.264 streams in both "main" (full-sized) and "sub" (lower resolution, compression quality, and/or frame rate) varieties. The "sub" stream is more suitable for fast computer vision work as well as remote/mobile streaming. Disk space these days is quite cheap (with 3 TB drives costing about $100), so we can afford to keep many camera-months of both streams on disk.
- decoding and analyzing only select "key" video frames (see wikipedia.
- off-loading expensive work to a GPU. Even the Raspberry Pi has a surprisingly powerful GPU.
- using HTTP Live Streaming rather than requiring custom browser plug-ins.
- taking advantage of cameras' built-in motion detection. This is the most obvious way to reduce motion detection CPU. It's a last resort because these cheap cameras' proprietary algorithms are awful compared to those described on changedetection.net. Cameras have high false-positive and false-negative rates, are hard to experiment with (as opposed to rerunning against saved video files), and don't provide any information beyond if motion exceeded the threshold or not.
Documentation
Getting help and getting involved
Please email the moonfire-nvr-users mailing list with questions, or just to say you love/hate the software and why. You can also file bugs and feature requests on the github issue tracker.
I'd welcome help with testing, development (in Rust, JavaScript, and HTML), user interface/graphic design, and documentation. Please email the mailing list if interested. Pull requests are welcome, but I encourage you to discuss large changes on the mailing list or in a github issue first to save effort.