4.9 KiB
Bucket Replication Guide 

Bucket replication is designed to replicate specific objects in buckets that are configured for replication.
To replicate objects in a bucket to a destination bucket on a target site either on the same cluster or a different cluster, start by creating version enabled buckets on both source and dest buckets. Next, the target site and destination bucket need to be configured on MinIO server by setting
Highlights
- Supports source and destination buckets to have the same name unlike AWS S3, addresses variety of usecases such as Splunk, Veeam site to site DR.
- Supports object locking/retention across source and destination buckets natively out of the box, unlike AWS S3.
- Simpler implementation than AWS S3 Bucket Replication Config with requirements such as IAM Role, AccessControlTranslation, Metrics and SourceSelectionCriteria are not needed with MinIO.
How to use?
Create a replication target on the source cluster as shown below:
mc admin bucket remote set myminio/srcbucket https://accessKey:secretKey@replica-endpoint:9000/destbucket --service replication --region us-east-1
Replication ARN = 'arn:minio:replication:us-east-1:c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket'
Note that the admin needs s3:GetReplicationConfigurationAction permission on source cluster. The credential used at the destination requires s3:ReplicateObject permission. Once successfully created and authorized this generates a replication target ARN. The command below lists all the currently authorized replication targets:
mc admin bucket remote list myminio/srcbucket --service "replication"
Replication ARN = 'arn:minio:replication:us-east-1:c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket'
The replication configuration can now be added to the source bucket by applying the json file with replication configuration. The ReplicationArn is passed in as a json element in the configuration.
{
"ReplicationArn" :"arn:minio:replication:us-east-1:c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket",
"Rules": [
{
"Status": "Enabled",
"Priority": 1,
"DeleteMarkerReplication": { "Status": "Disabled" },
"Filter" : {
"And": {
"Prefix": "Tax",
"Tags": [
{
"Key": "Year",
"Value": "2019"
},
{
"Key": "Company",
"Value": "AcmeCorp"
}
]
}
},
"Destination": {
"Bucket": "arn:aws:s3:::destbucket",
"StorageClass": "STANDARD"
}
}
]
}
mc replicate add myminio/srcbucket/Tax --priority 1 --arn "arn:minio:replication::c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket" --tags "Year=2019&Company=AcmeCorp" --storage-class "STANDARD"
Replication configuration applied successfully to myminio/srcbucket.
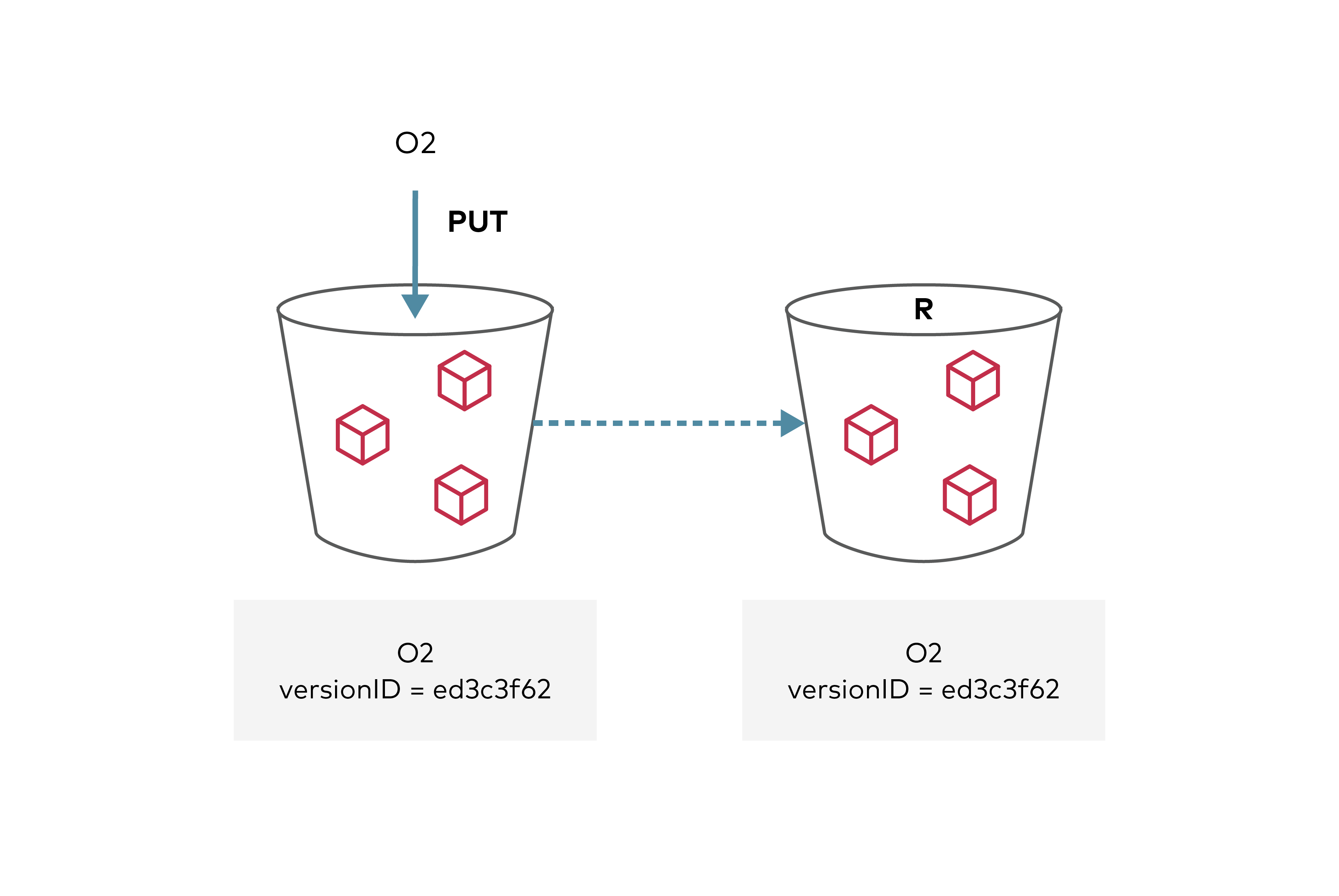
Apart from ReplicationArn , rest of the configuration follows AWS S3 Spec. Any objects uploaded to the source bucket that meet replication criteria will now be automatically replicated by the MinIO server to the remote destination bucket. Replication can be disabled at any time by disabling specific rules in the configuration or deleting the replication configuration entirely.
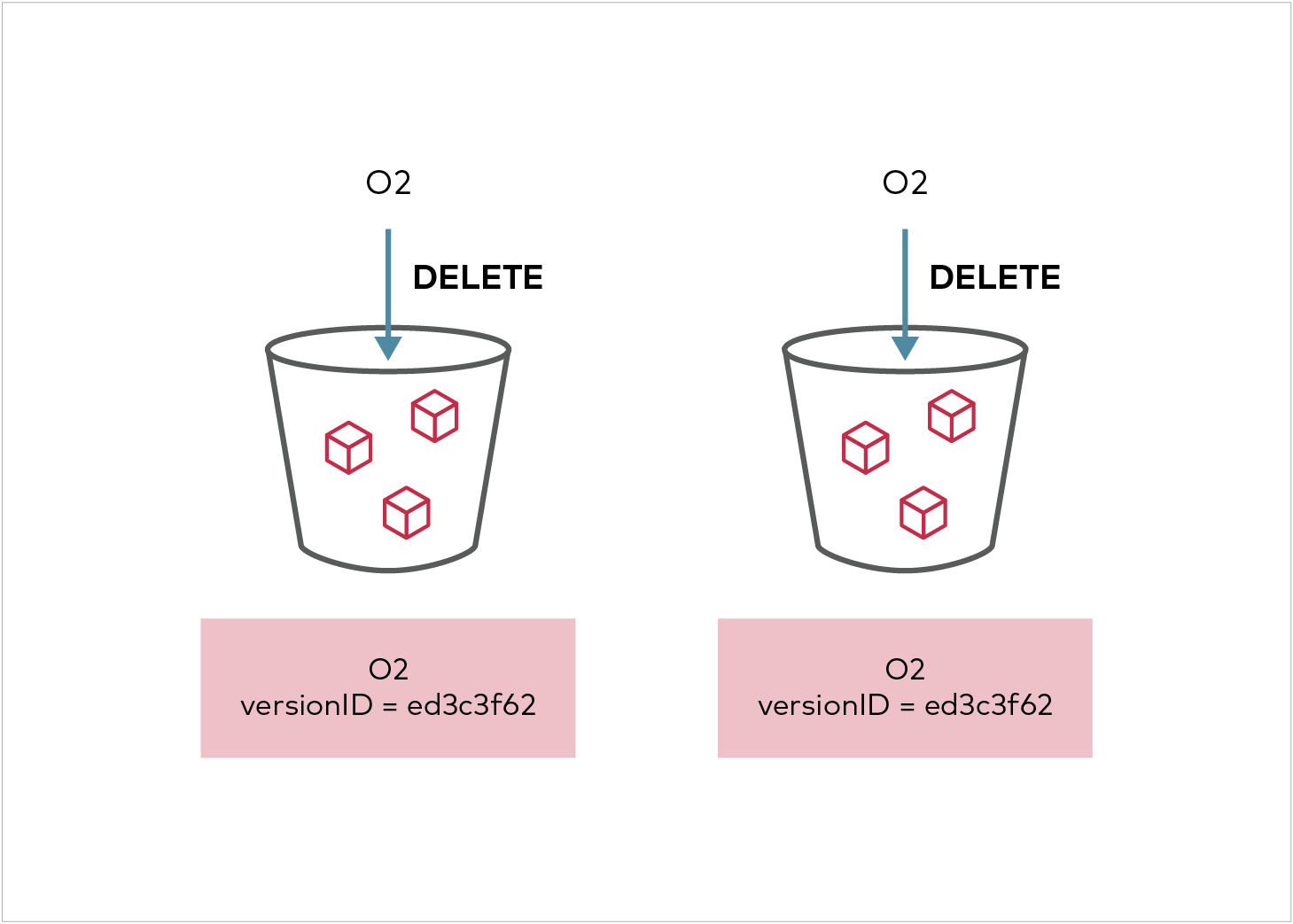
When an object is deleted from the source bucket, the replica will not be deleted as per S3 spec.
When object locking is used in conjunction with replication, both source and destination buckets needs to have object locking enabled. Similarly objects encrypted on the server side, will be replicated if destination also supports encryption.
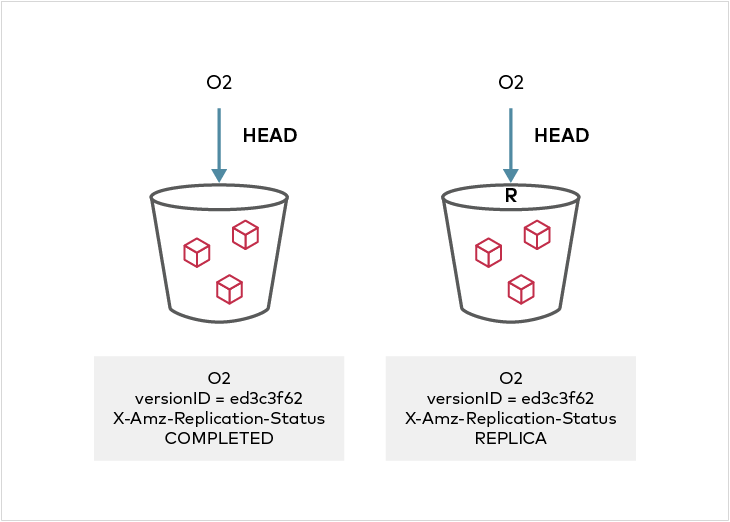
Replication status can be seen in the metadata on the source and destination objects. On the source side, the X-Amz-Replication-Status changes from PENDING to COMPLETE or FAILED after replication attempt either succeeded or failed respectively. On the destination side, a X-Amz-Replication-Status status of REPLICA indicates that the object was replicated successfully. Any replication failures are automatically re-attempted during a periodic disk crawl cycle.