With this change, MinIO's ILM supports transitioning objects to a remote tier. This change includes support for Azure Blob Storage, AWS S3 compatible object storage incl. MinIO and Google Cloud Storage as remote tier storage backends. Some new additions include: - Admin APIs remote tier configuration management - Simple journal to track remote objects to be 'collected' This is used by object API handlers which 'mutate' object versions by overwriting/replacing content (Put/CopyObject) or removing the version itself (e.g DeleteObjectVersion). - Rework of previous ILM transition to fit the new model In the new model, a storage class (a.k.a remote tier) is defined by the 'remote' object storage type (one of s3, azure, GCS), bucket name and a prefix. * Fixed bugs, review comments, and more unit-tests - Leverage inline small object feature - Migrate legacy objects to the latest object format before transitioning - Fix restore to particular version if specified - Extend SharedDataDirCount to handle transitioned and restored objects - Restore-object should accept version-id for version-suspended bucket (#12091) - Check if remote tier creds have sufficient permissions - Bonus minor fixes to existing error messages Co-authored-by: Poorna Krishnamoorthy <poorna@minio.io> Co-authored-by: Krishna Srinivas <krishna@minio.io> Signed-off-by: Harshavardhana <harsha@minio.io>
MinIO Deployment Quickstart Guide 

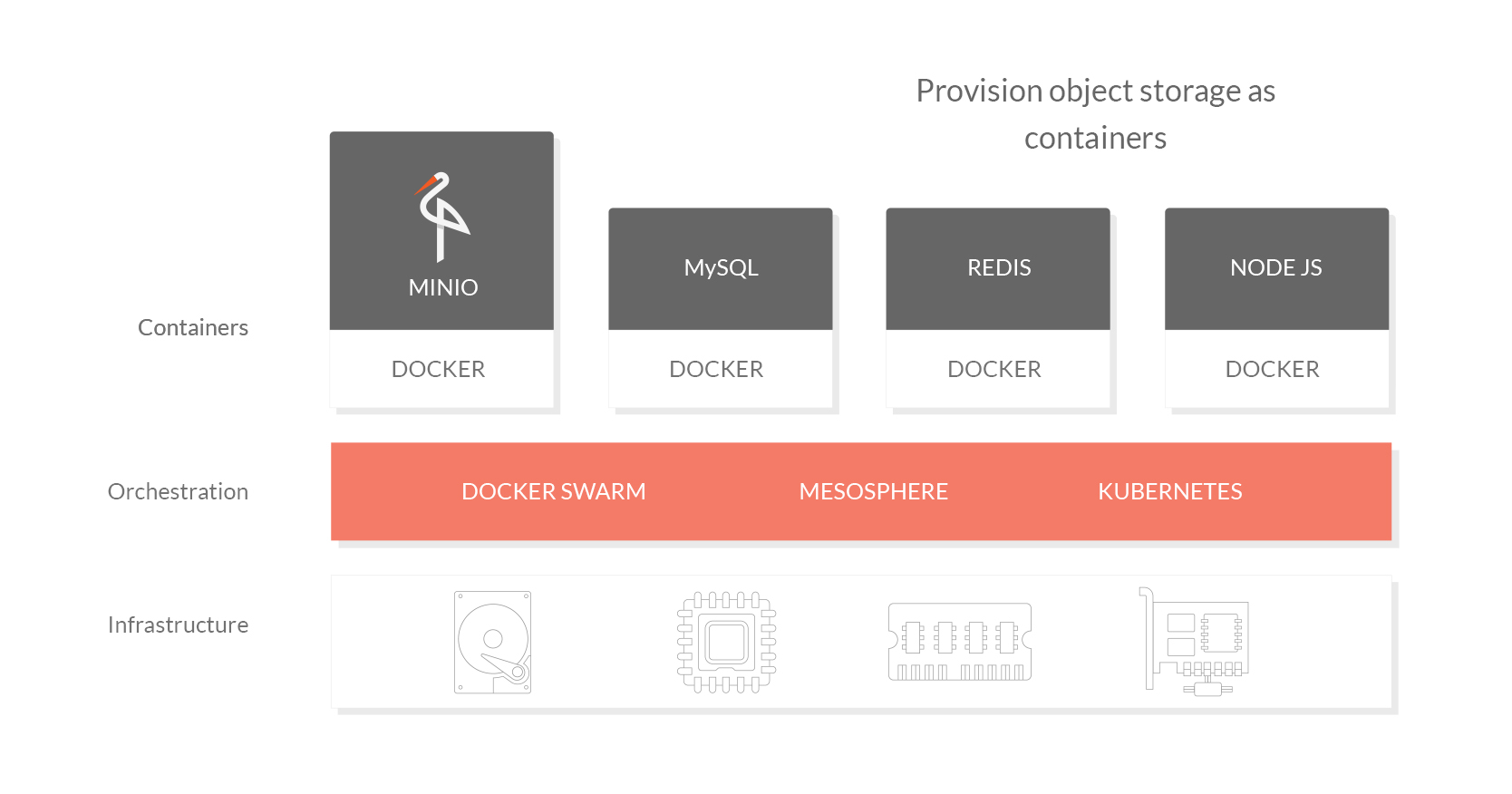
MinIO is a cloud-native application designed to scale in a sustainable manner in multi-tenant environments. Orchestration platforms provide perfect launchpad for MinIO to scale. Below is the list of MinIO deployment documents for various orchestration platforms:
| Orchestration platforms |
|---|
Docker Swarm |
Docker Compose |
Kubernetes |
Why is MinIO cloud-native?
The term cloud-native revolves around the idea of applications deployed as micro services, that scale well. It is not about just retrofitting monolithic applications onto modern container based compute environment. A cloud-native application is portable and resilient by design, and can scale horizontally by simply replicating. Modern orchestration platforms like Swarm, Kubernetes and DC/OS make replicating and managing containers in huge clusters easier than ever.
While containers provide isolated application execution environment, orchestration platforms allow seamless scaling by helping replicate and manage containers. MinIO extends this by adding isolated storage environment for each tenant.
MinIO is built ground up on the cloud-native premise. With features like erasure-coding, distributed and shared setup, it focuses only on storage and does it very well. While, it can be scaled by just replicating MinIO instances per tenant via an orchestration platform.
In a cloud-native environment, scalability is not a function of the application but the orchestration platform.
In a typical modern infrastructure deployment, application, database, key-store, etc. already live in containers and are managed by orchestration platforms. MinIO brings robust, scalable, AWS S3 compatible object storage to the lot.