GetActualSize() was heavily relying on o.Parts() to be non-empty to figure out if the object is multipart or not, However, we have many indicators of whether an object is multipart or not. Blindly assuming that o.Parts == nil is not a multipart, is an incorrect expectation instead, multipart must be obtained via - Stored metadata value indicating this is a multipart encrypted object. - Rely on <meta>-actual-size metadata to get the object's actual size. This value is preserved for additional reasons such as these. - ETag != 32 length
Bucket Replication Guide 

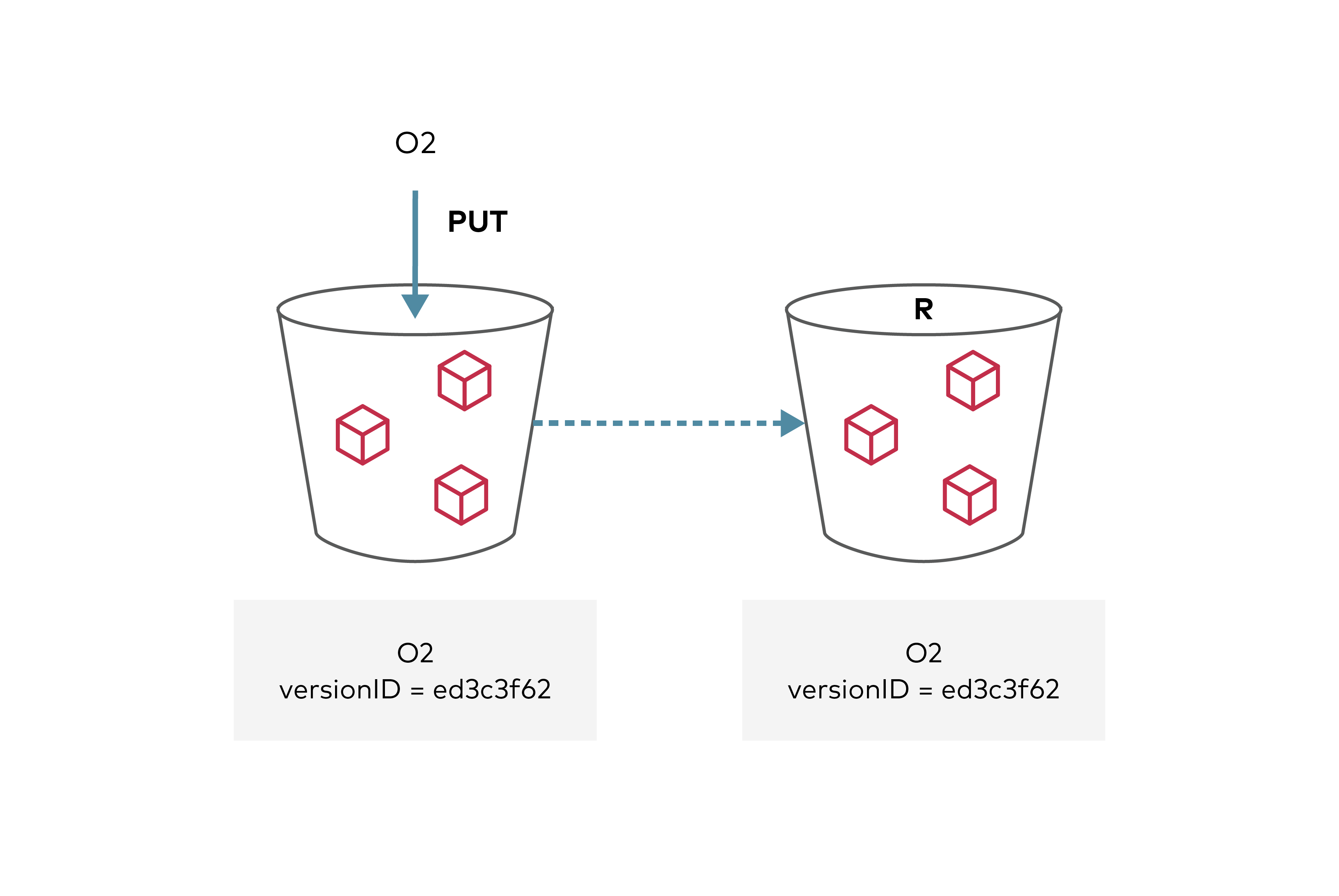
Bucket replication is designed to replicate selected objects in a bucket to a destination bucket.
The contents of this page have been migrated to the new MinIO Documentation: Bucket Replication page. The Bucket Replication page references dedicated tutorials for configuring one-way "Active-Passive" and two-way "Active-Active" bucket replication.
To replicate objects in a bucket to a destination bucket on a target site either in the same cluster or a different cluster, start by enabling versioning for both source and destination buckets. Finally, the target site and the destination bucket need to be configured on the source MinIO server.
Highlights
- Supports source and destination buckets to have the same name unlike AWS S3, addresses variety of usecases such as Splunk, Veeam site to site DR.
- Supports object locking/retention across source and destination buckets natively out of the box, unlike AWS S3.
- Simpler implementation than AWS S3 Bucket Replication Config with requirements such as IAM Role, AccessControlTranslation, Metrics and SourceSelectionCriteria are not needed with MinIO.
- Active-Active replication
- Multi destination replication
How to use?
Ensure that versioning is enabled on the source and target buckets with mc version command. If object locking is required, the buckets should have been created with mc mb --with-lock
The user setting up replication needs s3:GetReplicationConfiguration and s3:GetBucketVersioning permission on the source cluster. We do not recommend running root credentials/super admin with replication, instead create a dedicated user. The access credentials used at the destination requires s3:ReplicateObject permission.
The following minimal permission policy is needed by admin user setting up replication on the source:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": [
"admin:SetBucketTarget",
"admin:GetBucketTarget"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Sid": ""
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetReplicationConfiguration",
"s3:PutReplicationConfiguration",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:ListBucketMultipartUploads",
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:GetBucketVersioning"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::srcbucket"
]
}
]
}
The access key provided for the replication target cluster should have these minimal permissions:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetReplicationConfiguration",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:ListBucketMultipartUploads",
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:GetBucketVersioning",
"s3:GetBucketObjectLockConfiguration"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::destbucket"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:GetReplicationConfiguration",
"s3:ReplicateTags",
"s3:AbortMultipartUpload",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetObjectVersion",
"s3:GetObjectVersionTagging",
"s3:PutObject",
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:ReplicateObject",
"s3:ReplicateDelete"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::destbucket/*"
]
}
]
}
Please note that the permissions required by the admin user on the target cluster can be more fine grained to exclude permissions like "s3:ReplicateDelete", "s3:GetBucketObjectLockConfiguration" etc depending on whether delete replication rules are set up or if object locking is disabled on destbucket. The above policies assume that replication of objects, tags and delete marker replication are all enabled on object lock enabled buckets. A sample script to setup replication is provided here
To set up replication from a source bucket srcbucket on myminio cluster to a bucket destbucket on the target minio cluster with endpoint https://replica-endpoint:9000, use:
mc replicate add myminio/srcbucket --priority 1 --remote-bucket https://accessKey:secretKey@replica-endpoint:9000/destbucket
Replication configuration applied successfully to myminio/srcbucket.
Internally, this creates an ARN for the remote target associating the remote bucket as a replication target to the srcbucket on myminio.By default, if --replicate flag is not specified, replication of delete marker, permanent deletes, existing object replication and replica modification sync are all enabled. If you are using older mc versions, the ARN needs to be generated as a separate step before adding a replication rule.
NOTE: If you are using a mc version below
RELEASE.2022-12-24T15-21-38Z, the --remote-bucket flag needs an ARN generated bymc admin bucket remote addcommand. For mc versions RELEASE.2021-09-02T09-21-27Z and older, the remote target ARN needs to be passed in the --arn flag and actual remote bucket name in --remote-bucket flag ofmc replicate add. For example, in older releases of mc replication configuration used to be added with:
mc admin bucket remote add myminio/srcbucket https://accessKey:secretKey@replica-endpoint:9000/destbucket --service replication --region us-east-1
Remote ARN = 'arn:minio:replication:us-east-1:c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket'
mc replicate add myminio/srcbucket/Tax --priority 1 --remote-bucket destbucket --remote-bucket "arn:minio:replication:us-east-1:c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket" --tags "Year=2019&Company=AcmeCorp" --storage-class "STANDARD" --replicate "delete,delete-marker"
Replication configuration applied successfully to myminio/srcbucket.
The replication configuration generated has the following format and can be exported with mc replicate export command:
{
"Role" :"",
"Rules": [
{
"Status": "Enabled",
"Priority": 1,
"DeleteMarkerReplication": { "Status": "Disabled" },
"DeleteReplication": { "Status": "Disabled" },
"Filter" : {
"And": {
"Prefix": "Tax",
"Tags": [
{
"Key": "Year",
"Value": "2019"
},
{
"Key": "Company",
"Value": "AcmeCorp"
}
]
}
},
"Destination": {
"Bucket": "arn:minio:replication:us-east-1:c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket",
"StorageClass": "STANDARD"
},
"SourceSelectionCriteria": {
"ReplicaModifications": {
"Status": "Enabled"
}
}
}
]
}
The replication configuration follows AWS S3 Spec. Any objects uploaded to the source bucket that meet replication criteria will now be automatically replicated by the MinIO server to the remote destination bucket. Replication can be disabled at any time by disabling specific rules in the configuration or deleting the replication configuration entirely.
When object locking is used in conjunction with replication, both source and destination buckets needs to have object locking enabled. Similarly objects encrypted on the server side, will be replicated if destination also supports encryption.
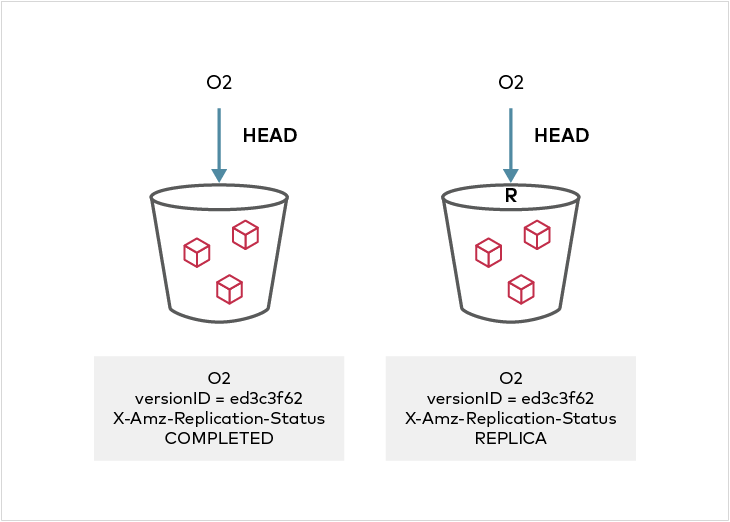
Replication status can be seen in the metadata on the source and destination objects. On the source side, the X-Amz-Replication-Status changes from PENDING to COMPLETED or FAILED after replication attempt either succeeded or failed respectively. On the destination side, a X-Amz-Replication-Status status of REPLICA indicates that the object was replicated successfully. Any replication failures are automatically re-attempted during a periodic disk scanner cycle.
To perform bi-directional replication, repeat the above process on the target site - this time setting the source bucket as the replication target. It is recommended that replication be run in a system with at least two CPU's available to the process, so that replication can run in its own thread.
Replica Modification sync
If bi-directional replication is set up between two clusters, any metadata update on the REPLICA object is by default reflected back in the source object when ReplicaModifications status in the SourceSelectionCriteria is Enabled. In MinIO, this is enabled by default. If a metadata update is performed on the "REPLICA" object, its X-Amz-Replication-Status will change from PENDING to COMPLETE or FAILED, and the source object version will show X-Amz-Replication-Status of REPLICA once the replication operation is complete.
The replication configuration in use on a bucket can be viewed using the mc replicate export alias/bucket command.
To disable replica metadata modification syncing, use mc replicate edit with the --replicate flag.
mc replicate edit alias/bucket --id xyz.id --replicate "delete,delete-marker"
To re-enable replica metadata modification syncing,
mc replicate edit alias/bucket --id xyz.id --replicate "delete,delete-marker,replica-metadata-sync"
MinIO Extension
Replicating Deletes
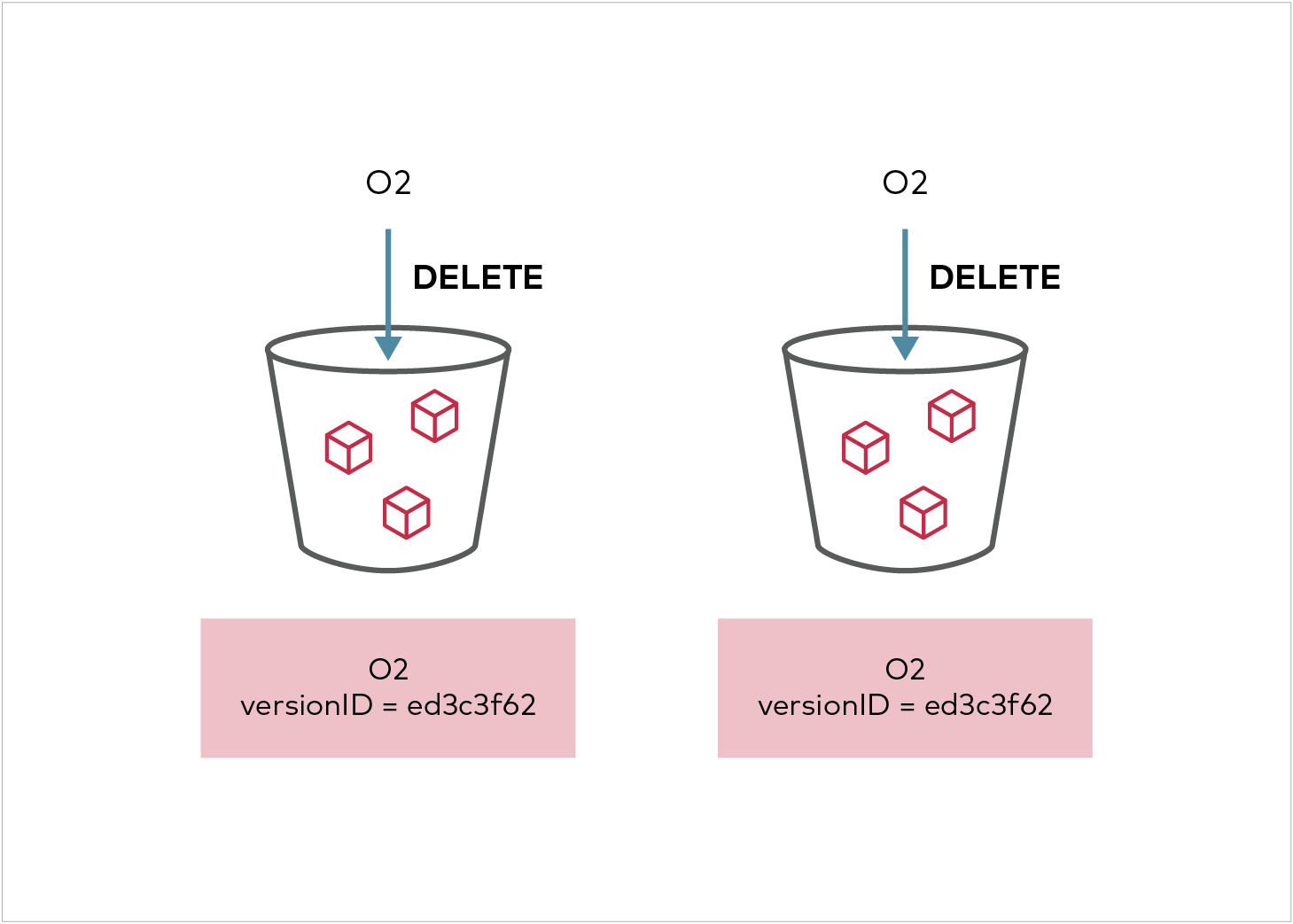
Delete marker replication is allowed in AWS V1 Configuration but not in V2 configuration. The MinIO implementation above is based on V2 configuration, however it has been extended to allow both DeleteMarker replication and replication of versioned deletes with the DeleteMarkerReplication and DeleteReplication fields in the replication configuration above. By default, this is set to Disabled unless the user specifies it while adding a replication rule.
When an object is deleted from the source bucket, the corresponding replica version will be marked deleted if delete marker replication is enabled in the replication configuration. Replication of deletes that specify a version id (a.k.a hard deletes) can be enabled by setting the DeleteReplication status to enabled in the replication configuration. This is a MinIO specific extension that can be enabled using the mc replicate add or mc replicate edit command with the --replicate "delete" flag.
Note that due to this extension behavior, AWS SDK's may not support the extension functionality pertaining to replicating versioned deletes.
Note that just like with AWS, Delete marker replication is disallowed in MinIO when the replication rule has tags.
To add a replication rule allowing both delete marker replication, versioned delete replication or both specify the --replicate flag with comma separated values as in the example below.
Additional permission of "s3:ReplicateDelete" action would need to be specified on the access key configured for the target cluster if Delete Marker replication or versioned delete replication is enabled.
mc replicate add myminio/srcbucket/Tax --priority 1 --remote-bucket `remote-target` --tags "Year=2019&Company=AcmeCorp" --storage-class "STANDARD" --replicate "delete,delete-marker"
Replication configuration applied successfully to myminio/srcbucket.
NOTE: In mc versions
RELEASE.2022-12-24T15-21-38Zand aboveremote-targetshould be of the formathttps://accessKey:secretKey@replica-endpoint:9000/destbucketwhich earlier used to be set duringmc admin bucket remote add. For older releases, use the arn generated withmc admin bucket remote addcommand - e.g."arn:minio:replication:us-east-1:c5be6b16-769d-432a-9ef1-4567081f3566:destbucket" as theremote-target.
Also note that mc version RELEASE.2021-09-02T09-21-27Z or older supports only a single remote target per bucket. To take advantage of multiple destination replication, use the latest version of mc
Status of delete marker replication can be viewed by doing a GET/HEAD on the object version - it will return a X-Minio-Replication-DeleteMarker-Status header and http response code of 405. In the case of permanent deletes, if the delete replication is pending or failed to propagate to the target cluster, GET/HEAD will return additional X-Minio-Replication-Delete-Status header and a http response code of 405.
The status of replication can be monitored by configuring event notifications on the source and target buckets using mc event add.On the source side, the s3:PutObject, s3:Replication:OperationCompletedReplication and s3:Replication:OperationFailedReplication events show the status of replication in the X-Amz-Replication-Status metadata.
On the target bucket, s3:PutObject event shows X-Amz-Replication-Status status of REPLICA in the metadata. Additional metrics to monitor backlog state for the purpose of bandwidth management and resource allocation are exposed via Prometheus - see https://github.com/minio/minio/blob/master/docs/metrics/prometheus/list.md for more details.
Sync/Async Replication
By default, replication is completed asynchronously. If synchronous replication is desired, set the --sync flag while adding a
remote replication target using the mc admin bucket remote add command. For mc releases on or after RELEASE.2022-12-24T15-21-38Z, the
--sync, --health-check and --bandwidth flags can be specified in mc replicate add|update command
mc admin bucket remote add myminio/srcbucket https://accessKey:secretKey@replica-endpoint:9000/destbucket --service replication --region us-east-1 --sync --healthcheck-seconds 100
Existing object replication
Existing object replication as detailed here can be enabled by passing existing-objects as a value to --replicate flag while adding or editing a replication rule.
Once existing object replication is enabled, all objects or object prefixes that satisfy the replication rules and were created prior to adding replication configuration OR while replication rules were disabled will be synced to the target cluster. Depending on the number of previously existing objects, the existing objects that are now eligible to be replicated will eventually be synced to the target cluster as the scanner schedules them. This may be slower depending on the load on the cluster, latency and size of the namespace.
In the rare event that target DR site is entirely lost and previously replicated objects to the DR cluster need to be re-replicated, mc replicate resync start alias/bucket --remote-bucket <arn> can be used to initiate a reset. This would initiate a re-sync between the two clusters by walking the bucket namespace and replicating eligible objects that satisfy the existing objects replication rule specified in the replication config. The status of the resync operation can be viewed with mc replicate resync status alias/bucket --remote-bucket <arn>.
Note that ExistingObjectReplication needs to be enabled in the config via mc replicate [add|edit] by passing existing-objects as one of the values to --replicate flag. Only those objects meeting replication rules and having existing object replication enabled will be re-synced.
Multi destination replication
Replication from a source bucket to multiple destination buckets is supported. For each of the targets, repeat the steps to configure a remote target ARN and add replication rules to the source bucket's replication config.
Note that on the source side, the X-Amz-Replication-Status changes from PENDING to COMPLETED after replication succeeds to each of the targets. On the destination side, a X-Amz-Replication-Status status of REPLICA indicates that the object was replicated successfully. Any replication failures are automatically re-attempted during a periodic disk scanner cycle.
Interaction with extended Bucket Versioning configuration
When Bucket Versioning with excluded prefixes are configured objects matching these prefixes are excluded from being versioned and replicated.
<VersioningConfiguration xmlns="http://s3.amazonaws.com/doc/2006-03-01/">
<Status>Enabled</Status>
<ExcludeFolders>true</ExcludeFolders>
<ExcludedPrefixes>
<Prefix>app1-jobs/*/_temporary/</Prefix>
</ExcludedPrefixes>
<ExcludedPrefixes>
<Prefix>app2-jobs/*/_magic/</Prefix>
</ExcludedPrefixes>
<!-- .. up to 10 prefixes in all -->
</VersioningConfiguration>
In the above sample config, objects under prefixes matching any of the ExcludedPrefixes glob patterns will neither be versioned nor replicated.
SSE-C Encryption
MinIO does not support SSE-C encrypted objects on replicated buckets, any application uploading SSE-C encrypted objects will be rejected with an error on replicated buckets.
Rationale
- SSE-C requires application to remember the keys for all GET/PUT operations, any unfortunate loss of keys would automatically mean the objects cannot be accessed anymore.
- SSE-C is hardly adopted by most widely used applications, applications prefer server to manage the keys via SSE-KMS or SSE-S3.
- MinIO recommends applications to use SSE-KMS, SSE-S3 for simpler, safer and robust encryption mechanism for replicated buckets.