diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index eb0ecc467..6bda14079 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Use the following commands to run a standalone MinIO server as a container.
Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication
require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically,
-with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide.html)
+with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Overview](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html)
for more complete documentation.
### Stable
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ root credentials. You can use the Browser to create buckets, upload objects, and
You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See
[Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers,
-see and click **MinIO SDKs** in the navigation to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
+see to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
> NOTE: To deploy MinIO on with persistent storage, you must map local persistent directories from the host OS to the container using the `podman -v` option. For example, `-v /mnt/data:/data` maps the host OS drive at `/mnt/data` to `/data` on the container.
@@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ see and click **MinIO SDKs** in the navigation to vi
Use the following commands to run a standalone MinIO server on macOS.
-Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide.html) for more complete documentation.
+Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Overview](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html) for more complete documentation.
### Homebrew (recommended)
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ brew install minio/stable/minio
The MinIO deployment starts using default root credentials `minioadmin:minioadmin`. You can test the deployment using the MinIO Console, an embedded web-based object browser built into MinIO Server. Point a web browser running on the host machine to and log in with the root credentials. You can use the Browser to create buckets, upload objects, and browse the contents of the MinIO server.
-You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see and click **MinIO SDKs** in the navigation to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
+You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
### Binary Download
@@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ chmod +x minio
The MinIO deployment starts using default root credentials `minioadmin:minioadmin`. You can test the deployment using the MinIO Console, an embedded web-based object browser built into MinIO Server. Point a web browser running on the host machine to and log in with the root credentials. You can use the Browser to create buckets, upload objects, and browse the contents of the MinIO server.
-You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see and click **MinIO SDKs** in the navigation to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
+You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
## GNU/Linux
@@ -99,9 +99,9 @@ The following table lists supported architectures. Replace the `wget` URL with t
The MinIO deployment starts using default root credentials `minioadmin:minioadmin`. You can test the deployment using the MinIO Console, an embedded web-based object browser built into MinIO Server. Point a web browser running on the host machine to and log in with the root credentials. You can use the Browser to create buckets, upload objects, and browse the contents of the MinIO server.
-You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see and click **MinIO SDKs** in the navigation to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
+You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
-> NOTE: Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide.html) for more complete documentation.
+> NOTE: Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Overview](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html#) for more complete documentation.
## Microsoft Windows
@@ -119,9 +119,9 @@ minio.exe server D:\
The MinIO deployment starts using default root credentials `minioadmin:minioadmin`. You can test the deployment using the MinIO Console, an embedded web-based object browser built into MinIO Server. Point a web browser running on the host machine to and log in with the root credentials. You can use the Browser to create buckets, upload objects, and browse the contents of the MinIO server.
-You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see and click **MinIO SDKs** in the navigation to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
+You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
-> NOTE: Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide.html) for more complete documentation.
+> NOTE: Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Overview](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html#) for more complete documentation.
## Install from Source
@@ -133,9 +133,9 @@ go install github.com/minio/minio@latest
The MinIO deployment starts using default root credentials `minioadmin:minioadmin`. You can test the deployment using the MinIO Console, an embedded web-based object browser built into MinIO Server. Point a web browser running on the host machine to and log in with the root credentials. You can use the Browser to create buckets, upload objects, and browse the contents of the MinIO server.
-You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see and click **MinIO SDKs** in the navigation to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
+You can also connect using any S3-compatible tool, such as the MinIO Client `mc` commandline tool. See [Test using MinIO Client `mc`](#test-using-minio-client-mc) for more information on using the `mc` commandline tool. For application developers, see to view MinIO SDKs for supported languages.
-> NOTE: Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide.html) for more complete documentation.
+> NOTE: Standalone MinIO servers are best suited for early development and evaluation. Certain features such as versioning, object locking, and bucket replication require distributed deploying MinIO with Erasure Coding. For extended development and production, deploy MinIO with Erasure Coding enabled - specifically, with a *minimum* of 4 drives per MinIO server. See [MinIO Erasure Code Overview](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html) for more complete documentation.
MinIO strongly recommends *against* using compiled-from-source MinIO servers for production environments.
@@ -222,7 +222,7 @@ For example: `export MINIO_SERVER_URL="https://minio.example.net"`
## Test using MinIO Client `mc`
-`mc` provides a modern alternative to UNIX commands like ls, cat, cp, mirror, diff etc. It supports filesystems and Amazon S3 compatible cloud storage services. Follow the MinIO Client [Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide) for further instructions.
+`mc` provides a modern alternative to UNIX commands like ls, cat, cp, mirror, diff etc. It supports filesystems and Amazon S3 compatible cloud storage services. Follow the MinIO Client [Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart) for further instructions.
## Upgrading MinIO
@@ -230,7 +230,7 @@ Upgrades require zero downtime in MinIO, all upgrades are non-disruptive, all tr
> NOTE: requires internet access to update directly from , optionally you can host any mirrors at
-- For deployments that installed the MinIO server binary by hand, use [`mc admin update`](https://docs.min.io/minio/baremetal/reference/minio-mc-admin/mc-admin-update.html)
+- For deployments that installed the MinIO server binary by hand, use [`mc admin update`](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin/mc-admin-update.html)
```sh
mc admin update
@@ -250,12 +250,10 @@ mc admin update
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO Erasure Code Overview](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
## Contribute to MinIO Project
diff --git a/cmd/server-startup-msg.go b/cmd/server-startup-msg.go
index 0b3185103..fa4801d8f 100644
--- a/cmd/server-startup-msg.go
+++ b/cmd/server-startup-msg.go
@@ -152,9 +152,9 @@ func printServerCommonMsg(apiEndpoints []string) {
}
}
-// Prints startup message for Object API acces, prints link to our SDK documentation.
+// Prints startup message for Object API access, prints link to our SDK documentation.
func printObjectAPIMsg() {
- logger.Info(color.Blue("\nDocumentation: ") + "https://docs.min.io")
+ logger.Info(color.Blue("\nDocumentation: ") + "https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html")
}
// Prints bucket notification configurations.
@@ -182,7 +182,7 @@ func printCLIAccessMsg(endPoint string, alias string) {
// Get saved credentials.
cred := globalActiveCred
- const mcQuickStartGuide = "https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide"
+ const mcQuickStartGuide = "https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart"
// Configure 'mc', following block prints platform specific information for minio client.
if color.IsTerminal() && !globalCLIContext.Anonymous {
diff --git a/cmd/update.go b/cmd/update.go
index 06d08edb6..f07466929 100644
--- a/cmd/update.go
+++ b/cmd/update.go
@@ -424,10 +424,10 @@ func getLatestReleaseTime(u *url.URL, timeout time.Duration, mode string) (sha25
const (
// Kubernetes deployment doc link.
- kubernetesDeploymentDoc = "https://docs.min.io/docs/deploy-minio-on-kubernetes"
+ kubernetesDeploymentDoc = "https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/index.html#quickstart-for-kubernetes"
// Mesos deployment doc link.
- mesosDeploymentDoc = "https://docs.min.io/docs/deploy-minio-on-dc-os"
+ mesosDeploymentDoc = "https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/index.html#quickstart-for-kubernetes"
)
func getDownloadURL(releaseTag string) (downloadURL string) {
diff --git a/docs/bigdata/README.md b/docs/bigdata/README.md
index 7f86e2f92..d77c5160a 100644
--- a/docs/bigdata/README.md
+++ b/docs/bigdata/README.md
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ MinIO also supports multi-cluster, multi-site federation similar to AWS regions
- [Setup Ambari](https://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/Ambari-2.7.1.0/bk_ambari-installation/content/set_up_the_ambari_server.html) which automatically sets up YARN
- [Installing Spark](https://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/HDP3/HDP-3.0.1/installing-spark/content/installing_spark.html)
- Install MinIO Distributed Server using one of the guides below.
- - [Deployment based on Kubernetes](https://docs.min.io/docs/deploy-minio-on-kubernetes.html#minio-distributed-server-deployment)
+ - [Deployment based on Kubernetes](https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/index.html#quickstart-for-kubernetes)
- [Deployment based on MinIO Helm Chart](https://github.com/helm/charts/tree/master/stable/minio)
## **3. Configure Hadoop, Spark, Hive to use MinIO**
diff --git a/docs/bucket/lifecycle/DESIGN.md b/docs/bucket/lifecycle/DESIGN.md
index 0f7ebf458..ff72a252d 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/lifecycle/DESIGN.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/lifecycle/DESIGN.md
@@ -51,5 +51,5 @@ Tiering and lifecycle transition are applicable only to erasure/distributed MinI
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO | Golang Client API Reference](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-api-reference.html#SetBucketLifecycle)
+- [MinIO | Golang Client API Reference](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/API.html#setbucketlifecycle-ctx-context-context-bucketname-config-lifecycle-configuration-error)
- [Object Lifecycle Management](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/object-lifecycle-mgmt.html)
diff --git a/docs/bucket/lifecycle/README.md b/docs/bucket/lifecycle/README.md
index a2c714669..457fd02eb 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/lifecycle/README.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/lifecycle/README.md
@@ -4,8 +4,8 @@ Enable object lifecycle configuration on buckets to setup automatic deletion of
## 1. Prerequisites
-- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
-- Install `mc` - [mc Quickstart Guide](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide.html)
+- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux).
+- Install `mc` - [mc Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
## 2. Enable bucket lifecycle configuration
@@ -59,7 +59,7 @@ TempUploads | temp/ | ✓ | ✓ | 7 day(s) | ✗
## 3. Activate ILM versioning features
-This will only work with a versioned bucket, take a look at [Bucket Versioning Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-bucket-versioning-guide.html) for more understanding.
+This will only work with a versioned bucket, take a look at [Bucket Versioning Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/object-management/object-versioning.html) for more understanding.
### 3.1 Automatic removal of non current objects versions
@@ -192,5 +192,5 @@ Note that transition event notification is a MinIO extension.
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO | Golang Client API Reference](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-api-reference.html#SetBucketLifecycle)
+- [MinIO | Golang Client API Reference](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/API.html)
- [Object Lifecycle Management](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/object-lifecycle-mgmt.html)
diff --git a/docs/bucket/notifications/README.md b/docs/bucket/notifications/README.md
index ec678da23..d0d58ef4c 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/notifications/README.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/notifications/README.md
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Various event types supported by MinIO server are
| `s3:BucketCreated` |
| `s3:BucketRemoved` |
-Use client tools like `mc` to set and listen for event notifications using the [`event` sub-command](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide#events). MinIO SDK's [`BucketNotification` APIs](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-api-reference#SetBucketNotification) can also be used. The notification message MinIO sends to publish an event is a JSON message with the following [structure](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/notification-content-structure.html).
+Use client tools like `mc` to set and listen for event notifications using the [`event` sub-command](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc/mc-event-add.html). MinIO SDK's [`BucketNotification` APIs](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/API.html#setbucketnotification-ctx-context-context-bucketname-string-config-notification-configuration-error) can also be used. The notification message MinIO sends to publish an event is a JSON message with the following [structure](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/notification-content-structure.html).
Bucket events can be published to the following targets:
@@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ Bucket events can be published to the following targets:
## Prerequisites
-- Install and configure MinIO Server from [here](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
-- Install and configure MinIO Client from [here](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide).
+- Install and configure MinIO Server from [here](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#procedure).
+- Install and configure MinIO Client from [here](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart).
```
$ mc admin config get myminio | grep notify
diff --git a/docs/bucket/quota/README.md b/docs/bucket/quota/README.md
index 5243f812b..a4924ef96 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/quota/README.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/quota/README.md
@@ -8,8 +8,8 @@ Buckets can be configured to have `Hard` quota - it disallows writes to the buck
## Prerequisites
-- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
+- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#procedure).
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
## Set bucket quota configuration
diff --git a/docs/bucket/replication/DESIGN.md b/docs/bucket/replication/DESIGN.md
index 6d773e8d5..8777caff6 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/replication/DESIGN.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/replication/DESIGN.md
@@ -156,5 +156,5 @@ If 3 or more targets are participating in active-active replication, the replica
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Bucket Versioning Implementation](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-bucket-versioning-guide.html)
-- [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide.html)
+- [MinIO Bucket Versioning Implementation](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/object-management/object-versioning.html)
+- [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
diff --git a/docs/bucket/replication/README.md b/docs/bucket/replication/README.md
index bd562b898..c4626f3cd 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/replication/README.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/replication/README.md
@@ -2,9 +2,9 @@
Bucket replication is designed to replicate selected objects in a bucket to a destination bucket.
-The contents of this page have been migrated to the new [MinIO Baremetal Documentation: Bucket Replication](https://docs.min.io/minio/baremetal/replication/replication-overview.html#) page. The [Bucket Replication](https://docs.min.io/minio/baremetal/replication/replication-overview.html#) section includes dedicated tutorials for configuring one-way "Active-Passive" and two-way "Active-Active" bucket replication. Please update your bookmarks to use the new MinIO documentation, as this legacy documentation will be deprecated and removed in the future.
+The contents of this page have been migrated to the new [MinIO Documentation: Bucket Replication](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/bucket-replication.html) page. The [Bucket Replication](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/bucket-replication/bucket-replication-requirements.html) page references dedicated tutorials for configuring one-way "Active-Passive" and two-way "Active-Active" bucket replication.
-To replicate objects in a bucket to a destination bucket on a target site either in the same cluster or a different cluster, start by enabling [versioning](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-bucket-versioning-guide.html) for both source and destination buckets. Finally, the target site and the destination bucket need to be configured on the source MinIO server.
+To replicate objects in a bucket to a destination bucket on a target site either in the same cluster or a different cluster, start by enabling [versioning](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/object-management/object-versioning.html) for both source and destination buckets. Finally, the target site and the destination bucket need to be configured on the source MinIO server.
## Highlights
@@ -152,11 +152,11 @@ The replication configuration can now be added to the source bucket by applying
The replication configuration follows [AWS S3 Spec](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/replication-add-config.html). Any objects uploaded to the source bucket that meet replication criteria will now be automatically replicated by the MinIO server to the remote destination bucket. Replication can be disabled at any time by disabling specific rules in the configuration or deleting the replication configuration entirely.
-When object locking is used in conjunction with replication, both source and destination buckets needs to have [object locking](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-bucket-object-lock-guide.html) enabled. Similarly objects encrypted on the server side, will be replicated if destination also supports encryption.
+When object locking is used in conjunction with replication, both source and destination buckets needs to have [object locking](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/object-management/object-retention.html) enabled. Similarly objects encrypted on the server side, will be replicated if destination also supports encryption.
Replication status can be seen in the metadata on the source and destination objects. On the source side, the `X-Amz-Replication-Status` changes from `PENDING` to `COMPLETED` or `FAILED` after replication attempt either succeeded or failed respectively. On the destination side, a `X-Amz-Replication-Status` status of `REPLICA` indicates that the object was replicated successfully. Any replication failures are automatically re-attempted during a periodic disk scanner cycle.
-To perform bi-directional replication, repeat the above process on the target site - this time setting the source bucket as the replication target. It is recommended that replication be run in a system with atleast two CPU's available to the process, so that replication can run in its own thread.
+To perform bi-directional replication, repeat the above process on the target site - this time setting the source bucket as the replication target. It is recommended that replication be run in a system with at least two CPU's available to the process, so that replication can run in its own thread.
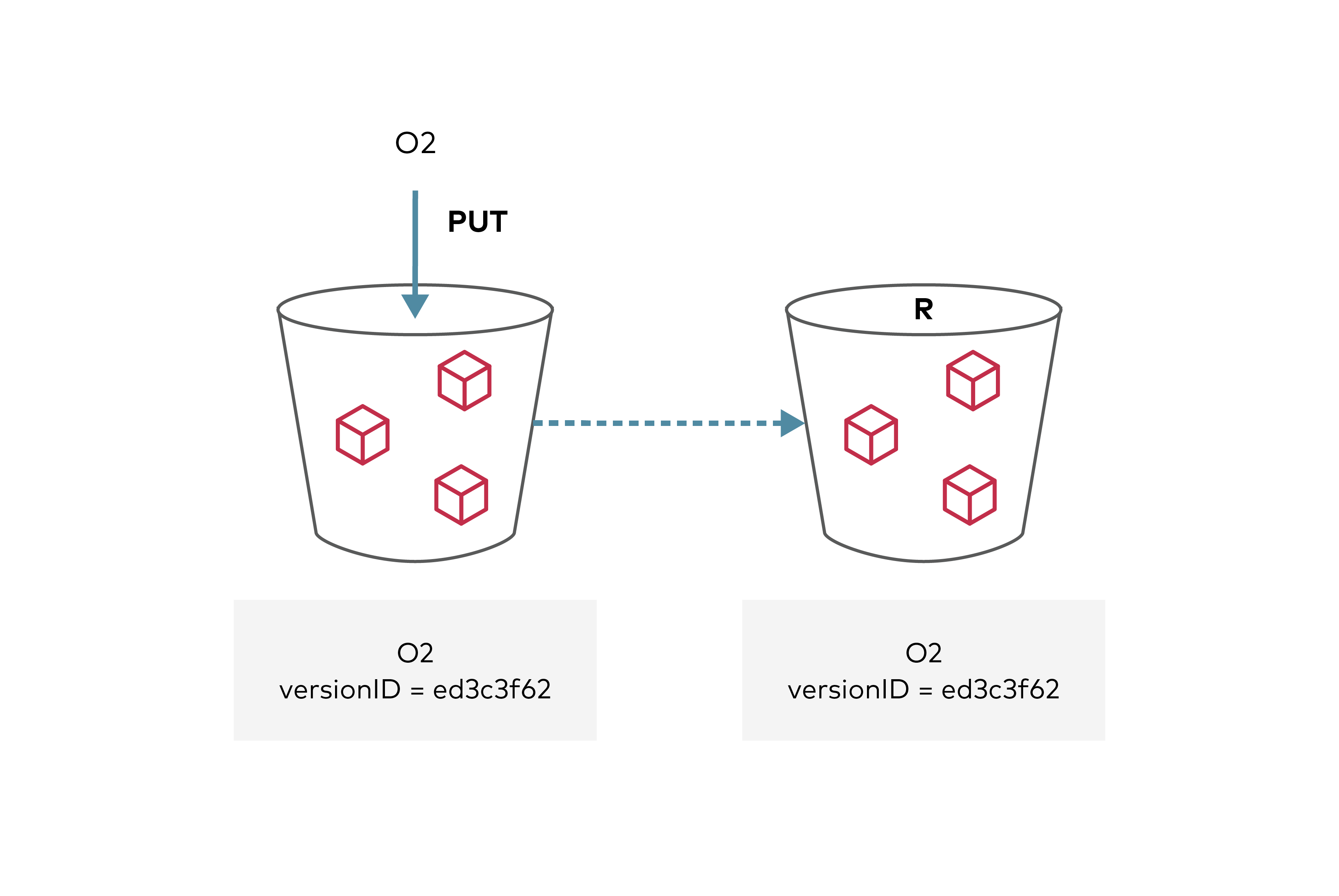
@@ -268,5 +268,5 @@ In the above sample config, objects under prefixes matching any of the `Excluded
## Explore Further
- [MinIO Bucket Replication Design](https://github.com/minio/minio/blob/master/docs/bucket/replication/DESIGN.md)
-- [MinIO Bucket Versioning Implementation](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-bucket-versioning-guide.html)
-- [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide.html)
+- [MinIO Bucket Versioning Implementation](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/object-management/object-retention.html)
+- [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
diff --git a/docs/bucket/retention/README.md b/docs/bucket/retention/README.md
index b54fa74ae..aa7e5328c 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/retention/README.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/retention/README.md
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ A default retention period and retention mode can be configured on a bucket to b
### 1. Prerequisites
-- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide)
+- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux)
- Install `awscli` - [Installing AWS Command Line Interface](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/cli-chap-install.html)
### 2. Set bucket WORM configuration
@@ -53,8 +53,7 @@ See
## Explore Further
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/bucket/versioning/README.md b/docs/bucket/versioning/README.md
index eaa25ed1c..1e4ee7c7c 100644
--- a/docs/bucket/versioning/README.md
+++ b/docs/bucket/versioning/README.md
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ public class IsVersioningEnabled {
## Explore Further
-- [Use `minio-java` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.minio.io/docs/java-client-quickstart-guide.html)
-- [Object Lock and Immutablity Guide](https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-bucket-object-lock-guide.html)
-- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `minio-java` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/java/minio-java.html)
+- [Object Lock and Immutablity Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/object-management/object-retention.html)
+- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/chroot/README.md b/docs/chroot/README.md
index 575ca3a18..c551ceb79 100644
--- a/docs/chroot/README.md
+++ b/docs/chroot/README.md
@@ -39,8 +39,8 @@ Instance is now accessible on the host at port 9000, proceed to access the Web b
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
+- [MinIO Erasure Code Overview](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/compression/README.md b/docs/compression/README.md
index 8b6509615..10c71a42f 100644
--- a/docs/compression/README.md
+++ b/docs/compression/README.md
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ will increase speed when the content can be compressed.
### 1. Prerequisites
-Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
+Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux).
### 2. Run MinIO with compression
@@ -127,8 +127,7 @@ the data directory to view the size of the object.
## Explore Further
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/config/README.md b/docs/config/README.md
index 04be1e9cd..ae610bfce 100644
--- a/docs/config/README.md
+++ b/docs/config/README.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ MinIO stores all its config as part of the server deployment, config is erasure
### Certificate Directory
-TLS certificates by default are expected to be stored under ``${HOME}/.minio/certs`` directory. You need to place certificates here to enable `HTTPS` based access. Read more about [How to secure access to MinIO server with TLS](https://docs.min.io/docs/how-to-secure-access-to-minio-server-with-tls).
+TLS certificates by default are expected to be stored under ``${HOME}/.minio/certs`` directory. You need to place certificates here to enable `HTTPS` based access. Read more about [How to secure access to MinIO server with TLS](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/network-encryption.html).
Following is a sample directory structure for MinIO server with TLS certificates.
@@ -181,7 +181,7 @@ MINIO_API_REMOTE_TRANSPORT_DEADLINE (duration) set the deadline for API reques
#### Notifications
-Notification targets supported by MinIO are in the following list. To configure individual targets please refer to more detailed documentation [here](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-bucket-notification-guide.html).
+Notification targets supported by MinIO are in the following list. To configure individual targets please refer to more detailed documentation [here](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/monitoring.html#bucket-notifications).
```
notify_webhook publish bucket notifications to webhook endpoints
@@ -345,5 +345,5 @@ minio server /data
## Explore Further
-* [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide)
-* [Configure MinIO Server with TLS](https://docs.min.io/docs/how-to-secure-access-to-minio-server-with-tls)
+* [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux)
+* [Configure MinIO Server with TLS](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/network-encryption.htmls)
diff --git a/docs/disk-caching/README.md b/docs/disk-caching/README.md
index 02e218d10..8f2bd6cfe 100644
--- a/docs/disk-caching/README.md
+++ b/docs/disk-caching/README.md
@@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ Disk caching feature here refers to the use of caching disks to store content cl
### 1. Prerequisites
-Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
+Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linuxe).
### 2. Run MinIO gateway with cache
@@ -34,13 +34,12 @@ In the example above this means that `MINIO_CACHE_WATERMARK_LOW` is effectively
### 3. Test your setup
-To test this setup, access the MinIO gateway via browser or [`mc`](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide). You’ll see the uploaded files are accessible from all the MinIO endpoints.
+To test this setup, access the MinIO gateway via browser or [`mc`](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart). You’ll see the uploaded files are accessible from all the MinIO endpoints.
## Explore Further
- [Disk cache design](https://github.com/minio/minio/blob/master/docs/disk-caching/DESIGN.md)
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/distributed/README.md b/docs/distributed/README.md
index fe1e39eb9..5b2059972 100644
--- a/docs/distributed/README.md
+++ b/docs/distributed/README.md
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ MinIO in distributed mode can help you setup a highly-available storage system w
### Data protection
-Distributed MinIO provides protection against multiple node/drive failures and [bit rot](https://github.com/minio/minio/blob/master/docs/erasure/README.md#what-is-bit-rot-protection) using [erasure code](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide). As the minimum disks required for distributed MinIO is 2 (same as minimum disks required for erasure coding), erasure code automatically kicks in as you launch distributed MinIO.
+Distributed MinIO provides protection against multiple node/drive failures and [bit rot](https://github.com/minio/minio/blob/master/docs/erasure/README.md#what-is-bit-rot-protection) using [erasure code](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html). As the minimum disks required for distributed MinIO is 2 (same as minimum disks required for erasure coding), erasure code automatically kicks in as you launch distributed MinIO.
If one or more disks are offline at the start of a PutObject or NewMultipartUpload operation the object will have additional data protection bits added automatically to provide additional safety for these objects.
@@ -34,7 +34,15 @@ If you're aware of stand-alone MinIO set up, the process remains largely the sam
### 1. Prerequisites
-Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
+Install MinIO either on Kubernetes or Distributed Linux.
+
+Install MinIO on Kubernetes:
+
+- [MinIO Quickstart Guide for Kubernetes](https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/index.html#quickstart-for-kubernetes).
+- [Deploy a Tenant from the MinIO Operator](https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/operations/install-deploy-manage/deploy-minio-tenant.html)
+
+Install Distributed MinIO on Linux:
+- [Deploy Distributed MinIO on Linux](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/install-deploy-manage/deploy-minio-multi-node-multi-drive.html#deploy-distributed-minio)
### 2. Run distributed MinIO
@@ -90,13 +98,12 @@ Now the server has expanded total storage by _(newly_added_servers\*m)_ more dis
## 3. Test your setup
-To test this setup, access the MinIO server via browser or [`mc`](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide).
+To test this setup, access the MinIO server via browser or [`mc`](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart).
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/docker/README.md b/docs/docker/README.md
index bfad65ac0..093467579 100644
--- a/docs/docker/README.md
+++ b/docs/docker/README.md
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ Docker installed on your machine. Download the relevant installer from [here](ht
## Run Standalone MinIO on Docker
-*Note*: Standalone MinIO is intended for early development and evaluation. For production clusters, deploy a [Distributed](https://docs.min.io/minio/baremetal/installation/deployment-and-management.html) MinIO deployment.
+*Note*: Standalone MinIO is intended for early development and evaluation. For production clusters, deploy a [Distributed](https://min.io/docs/minio/container/operations/install-deploy-manage/deploy-minio-single-node-multi-drive.html) MinIO deployment.
MinIO needs a persistent volume to store configuration and application data. For testing purposes, you can launch MinIO by simply passing a directory (`/data` in the example below). This directory gets created in the container filesystem at the time of container start. But all the data is lost after container exits.
@@ -53,9 +53,11 @@ docker run \
quay.io/minio/minio server /data --console-address ":9001"
```
-## Run Distributed MinIO on Docker
+## Run Distributed MinIO on Containers
-Distributed MinIO can be deployed via [Docker Compose](https://docs.min.io/docs/deploy-minio-on-docker-compose). This means Docker Compose lets you quickly get started with Distributed MinIO on your computer - ideal for development, testing, staging environments. We recommend kubernetes based deployment for production level deployment .
+We recommend kubernetes based deployment for production level deployment .
+
+See the [Kubernetes documentation](https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/index.html) for more information.
## MinIO Docker Tips
@@ -209,6 +211,5 @@ docker stats
## Explore Further
-* [Deploy MinIO on Docker Compose](https://docs.min.io/docs/deploy-minio-on-docker-compose)
-* [Distributed MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/distributed-minio-quickstart-guide)
-* [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide)
+* [Distributed MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/container/operations/install-deploy-manage/deploy-minio-single-node-multi-drive.html)
+* [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/container/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html)
diff --git a/docs/erasure/README.md b/docs/erasure/README.md
index fa2625b0d..cbee49ac1 100644
--- a/docs/erasure/README.md
+++ b/docs/erasure/README.md
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ MinIO's erasure coded backend uses high speed [HighwayHash](https://github.com/m
MinIO divides the drives you provide into erasure-coding sets of *2 to 16* drives. Therefore, the number of drives you present must be a multiple of one of these numbers. Each object is written to a single erasure-coding set.
-Minio uses the largest possible EC set size which divides into the number of drives given. For example, *18 drives* are configured as *2 sets of 9 drives*, and *24 drives* are configured as *2 sets of 12 drives*. This is true for scenarios when running MinIO as a standalone erasure coded deployment. In [distributed setup however node (affinity) based](https://docs.minio.io/docs/distributed-minio-quickstart-guide.html) erasure stripe sizes are chosen.
+Minio uses the largest possible EC set size which divides into the number of drives given. For example, *18 drives* are configured as *2 sets of 9 drives*, and *24 drives* are configured as *2 sets of 12 drives*. This is true for scenarios when running MinIO as a standalone erasure coded deployment. In [distributed setup however node (affinity) based](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/install-deploy-manage/deploy-minio-multi-node-multi-drive.html) erasure stripe sizes are chosen.
The drives should all be of approximately the same size.
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ The drives should all be of approximately the same size.
### 1. Prerequisites
-Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide)
+Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux)
### 2. Run MinIO Server with Erasure Code
diff --git a/docs/erasure/storage-class/README.md b/docs/erasure/storage-class/README.md
index 8e6e55440..1607d9c9e 100644
--- a/docs/erasure/storage-class/README.md
+++ b/docs/erasure/storage-class/README.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
MinIO server supports storage class in erasure coding mode. This allows configurable data and parity disks per object.
-This page is intended as a summary of MinIO Erasure Coding. For a more complete explanation, see .
+This page is intended as a summary of MinIO Erasure Coding. For a more complete explanation, see .
## Overview
@@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ The default value for the `STANDARD` storage class depends on the number of volu
| 6-7 | EC:3 |
| 8 or more | EC:4 |
-For more complete documentation on Erasure Set sizing, see the [MinIO Documentation on Erasure Sets](https://docs.min.io/minio/baremetal/concepts/erasure-coding.html#erasure-sets).
+For more complete documentation on Erasure Set sizing, see the [MinIO Documentation on Erasure Sets](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html#erasure-sets).
### Allowed values for REDUCED_REDUNDANCY storage class
diff --git a/docs/federation/lookup/README.md b/docs/federation/lookup/README.md
index 32f6fe388..5ab514fab 100644
--- a/docs/federation/lookup/README.md
+++ b/docs/federation/lookup/README.md
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ This document explains how to configure MinIO with `Bucket lookup from DNS` styl
### 1. Prerequisites
-Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
+Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux).
### 2. Run MinIO in federated mode
@@ -76,12 +76,11 @@ it is randomized which cluster might provision the bucket.
### 3. Test your setup
-To test this setup, access the MinIO server via browser or [`mc`](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide). You’ll see the uploaded files are accessible from the all the MinIO endpoints.
+To test this setup, access the MinIO server via browser or [`mc`](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart). You’ll see the uploaded files are accessible from the all the MinIO endpoints.
## Explore Further
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/gateway/README.md b/docs/gateway/README.md
index 9ad8a4152..7ee8d49f6 100644
--- a/docs/gateway/README.md
+++ b/docs/gateway/README.md
@@ -1,5 +1,8 @@
# MinIO Gateway [](https://slack.min.io)
+**The MinIO Gateway has been deprecated as of February 2022 and removed from MinIO files as of July 2022.**
+**See https://blog.min.io/deprecation-of-the-minio-gateway/ for more information.**
+
## Support
Gateway implementations are frozen and are not accepting any new features. Please reports any bugs at . If you are an existing customer please login to for production support.
diff --git a/docs/gateway/nas.md b/docs/gateway/nas.md
index 7740144cb..3f1377720 100644
--- a/docs/gateway/nas.md
+++ b/docs/gateway/nas.md
@@ -109,6 +109,6 @@ NAS gateway implementation allows symlinks on regular files.
## Explore Further
-- [`mc` command-line interface](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [`aws` command-line interface](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [`minio-go` Go SDK](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
+- [`mc` command-line interface](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
+- [`aws` command-line interface](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [`minio-go` Go SDK](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
diff --git a/docs/gateway/s3.md b/docs/gateway/s3.md
index 8a7eadb6f..616f2218a 100644
--- a/docs/gateway/s3.md
+++ b/docs/gateway/s3.md
@@ -137,8 +137,6 @@ MinIO edge caching allows storing content closer to the applications. Frequently
- Dramatic improvements for time to first byte for any object.
- Avoid S3 [data transfer charges](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/pricing/).
-Refer [this document](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-disk-cache-guide.html) to get started with MinIO Caching.
-
## MinIO Console
MinIO Gateway comes with an embedded web based object browser. Point your web browser to to ensure that your server has started successfully.
@@ -157,6 +155,6 @@ With MinIO S3 gateway, you can use MinIO Console to explore AWS S3 based objects
## Explore Further
-- [`mc` command-line interface](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [`aws` command-line interface](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [`minio-go` Go SDK](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
+- [`mc` command-line interface](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [`aws` command-line interface](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [`minio-go` Go SDK](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
diff --git a/docs/integrations/veeam/README.md b/docs/integrations/veeam/README.md
index 2603fef8d..830130e86 100644
--- a/docs/integrations/veeam/README.md
+++ b/docs/integrations/veeam/README.md
@@ -5,10 +5,10 @@ When using Veeam Backup and Replication, you can use S3 compatible object storag
## Prerequisites
- One or both of Veeam Backup and Replication with support for S3 compatible object store (e.g. 9.5.4) and Veeam Backup for Office365 (VBO)
-- MinIO object storage set up per
-- Veeam requires TLS connections to the object storage. This can be configured per
+- MinIO object storage set up per
+- Veeam requires TLS connections to the object storage. This can be configured per
- The S3 bucket, Access Key and Secret Key have to be created before and outside of Veeam.
-- Configure the minio client for the Veeam MinIO endpoint -
+- Configure the minio client for the Veeam MinIO endpoint -
## Setting up an S3 compatible object store for Veeam Backup and Replication
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ mc mb myminio/veeambackup
mc mb -l myminio/veeambackup
```
-> Object locking requires erasure coding enabled on the minio server. For more information see .
+> Object locking requires erasure coding enabled on the minio server. For more information see .
### Add MinIO as an object store for Veeam
diff --git a/docs/kms/README.md b/docs/kms/README.md
index 9d63bac46..bb1d58c54 100644
--- a/docs/kms/README.md
+++ b/docs/kms/README.md
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ MinIO uses a key-management-system (KMS) to support SSE-S3. If a client requests
## Quick Start
-MinIO supports multiple KMS implementations via our [KES](https://github.com/minio/kes#kes) project. We run a KES instance at `https://play.min.io:7373` for you to experiment and quickly get started. To run MinIO with a KMS just fetch the root identity, set the following environment variables and then start your MinIO server. If you havn't installed MinIO, yet, then follow the MinIO [install instructions](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide) first.
+MinIO supports multiple KMS implementations via our [KES](https://github.com/minio/kes#kes) project. We run a KES instance at `https://play.min.io:7373` for you to experiment and quickly get started. To run MinIO with a KMS just fetch the root identity, set the following environment variables and then start your MinIO server. If you havn't installed MinIO, yet, then follow the MinIO [install instructions](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux) first.
### 1. Fetch the root identity
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@ The MinIO-KES configuration is always the same - regardless of the underlying KM
### Further references
-- [Run MinIO with TLS / HTTPS](https://docs.min.io/docs/how-to-secure-access-to-minio-server-with-tls.html)
+- [Run MinIO with TLS / HTTPS](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/network-encryption.html)
- [Tweak the KES server configuration](https://github.com/minio/kes/wiki/Configuration)
- [Run a load balancer infront of KES](https://github.com/minio/kes/wiki/TLS-Proxy)
- [Understand the KES server concepts](https://github.com/minio/kes/wiki/Concepts)
@@ -137,8 +137,7 @@ Certificates are no secrets and sent in plaintext as part of the TLS handshake.
## Explore Further
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/logging/README.md b/docs/logging/README.md
index 8dcd3ae59..52d861e4d 100644
--- a/docs/logging/README.md
+++ b/docs/logging/README.md
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ Console target is on always and cannot be disabled.
HTTP target logs to a generic HTTP endpoint in JSON format and is not enabled by default. To enable HTTP target logging you would have to update your MinIO server configuration using `mc admin config set` command.
-Assuming `mc` is already [configured](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide.html)
+Assuming `mc` is already [configured](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
```
mc admin config get myminio/ logger_webhook
@@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ minio server /mnt/data
## Audit Targets
-Assuming `mc` is already [configured](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide.html)
+Assuming `mc` is already [configured](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
### Audit HTTP Target
@@ -223,5 +223,5 @@ NOTE:
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide)
-- [Configure MinIO Server with TLS](https://docs.min.io/docs/how-to-secure-access-to-minio-server-with-tls)
+- [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux)
+- [Configure MinIO Server with TLS](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/network-encryption.html)
diff --git a/docs/metrics/prometheus/README.md b/docs/metrics/prometheus/README.md
index a4eba5709..4ae6f2d8b 100644
--- a/docs/metrics/prometheus/README.md
+++ b/docs/metrics/prometheus/README.md
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ MinIO exports Prometheus compatible data by default as an authorized endpoint at
## Prerequisites
-To get started with MinIO, refer [MinIO QuickStart Document](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
+To get started with MinIO, refer [MinIO QuickStart Document](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux).
Follow below steps to get started with MinIO monitoring using Prometheus.
### 1. Download Prometheus
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ minio server ~/test
> If MinIO is configured to expose metrics without authentication, you don't need to use `mc` to generate prometheus config. You can skip reading further and move to 3.2 section.
-The Prometheus endpoint in MinIO requires authentication by default. Prometheus supports a bearer token approach to authenticate prometheus scrape requests, override the default Prometheus config with the one generated using mc. To generate a Prometheus config for an alias, use [mc](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide) as follows `mc admin prometheus generate `.
+The Prometheus endpoint in MinIO requires authentication by default. Prometheus supports a bearer token approach to authenticate prometheus scrape requests, override the default Prometheus config with the one generated using mc. To generate a Prometheus config for an alias, use [mc](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart) as follows `mc admin prometheus generate `.
The command will generate the `scrape_configs` section of the prometheus.yml as follows:
diff --git a/docs/minio-limits.md b/docs/minio-limits.md
index efaaca1c8..fbd80e066 100644
--- a/docs/minio-limits.md
+++ b/docs/minio-limits.md
@@ -39,15 +39,15 @@ We found the following APIs to be redundant or less useful outside of AWS S3. If
### List of Amazon S3 Bucket API's not supported on MinIO
-- BucketACL (Use [bucket policies](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide#policy) instead)
+- BucketACL (Use [bucket policies](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/identity-access-management/policy-based-access-control.html) instead)
- BucketCORS (CORS enabled by default on all buckets for all HTTP verbs)
- BucketWebsite (Use [`caddy`](https://github.com/caddyserver/caddy) or [`nginx`](https://www.nginx.com/resources/wiki/))
-- BucketAnalytics, BucketMetrics, BucketLogging (Use [bucket notification](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide#events) APIs)
+- BucketAnalytics, BucketMetrics, BucketLogging (Use [bucket notification](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/monitoring/bucket-notifications.html) APIs)
- BucketRequestPayment
### List of Amazon S3 Object API's not supported on MinIO
-- ObjectACL (Use [bucket policies](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide#policy) instead)
+- ObjectACL (Use [bucket policies](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/identity-access-management/policy-based-access-control.html) instead)
## Object name restrictions on MinIO
diff --git a/docs/multi-tenancy/README.md b/docs/multi-tenancy/README.md
index 595f13a3e..9af1e15d8 100644
--- a/docs/multi-tenancy/README.md
+++ b/docs/multi-tenancy/README.md
@@ -64,4 +64,4 @@ minio server --address :9003 http://192.168.10.1{1...4}/data/tenant3
## Cloud Scale Deployment
-A container orchestration platform (e.g. Kubernetes) is recommended for large-scale, multi-tenant MinIO deployments. See the [MinIO Deployment Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-deployment-quickstart-guide) to get started with MinIO on orchestration platforms.
+A container orchestration platform (e.g. Kubernetes) is recommended for large-scale, multi-tenant MinIO deployments. See the [MinIO Deployment Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/container/index.html#quickstart-for-linux) to get started with MinIO on orchestration platforms.
diff --git a/docs/multi-user/README.md b/docs/multi-user/README.md
index 486aefb50..56f6c720e 100644
--- a/docs/multi-user/README.md
+++ b/docs/multi-user/README.md
@@ -8,13 +8,13 @@ In this document we will explain in detail on how to configure multiple users.
### 1. Prerequisites
-- Install mc - [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide.html)
-- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide)
+- Install mc - [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
+- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux)
- Configure etcd (optional needed only in gateway or federation mode) - [Etcd V3 Quickstart Guide](https://github.com/minio/minio/blob/master/docs/sts/etcd.md)
### 2. Create a new user with canned policy
-Use [`mc admin policy`](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html#policies) to create canned policies. Server provides a default set of canned policies namely `writeonly`, `readonly` and `readwrite` *(these policies apply to all resources on the server)*. These can be overridden by custom policies using `mc admin policy` command.
+Use [`mc admin policy`](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin/mc-admin-policy.html) to create canned policies. Server provides a default set of canned policies namely `writeonly`, `readonly` and `readwrite` *(these policies apply to all resources on the server)*. These can be overridden by custom policies using `mc admin policy` command.
Create new canned policy file `getonly.json`. This policy enables users to download all objects under `my-bucketname`.
@@ -267,7 +267,7 @@ If the user is authenticating using an STS credential which was authorized from
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Client Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide)
-- [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-sts-quickstart-guide)
-- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO Client Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/security-token-service.html)
+- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/multi-user/admin/README.md b/docs/multi-user/admin/README.md
index 742c20114..122b7b14f 100644
--- a/docs/multi-user/admin/README.md
+++ b/docs/multi-user/admin/README.md
@@ -8,12 +8,12 @@ In this document we will explain in detail on how to configure admin users.
### 1. Prerequisites
-- Install mc - [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide.html)
-- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide)
+- Install mc - [MinIO Client Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart)
+- Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux)
### 2. Create a new admin user with CreateUser, DeleteUser and ConfigUpdate permissions
-Use [`mc admin policy`](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html#policies) to create custom admin policies.
+Use [`mc admin policy`](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin/mc-admin-policy.html#command-mc.admin.policy) to create custom admin policies.
Create new canned policy file `adminManageUser.json`. This policy enables admin user to
manage other users.
@@ -162,11 +162,11 @@ mc admin policy set myminio-admin1 user1policy user=user1
### 5. Using an external IDP for admin users
Admin users can also be externally managed by an IDP by configuring admin policy with
-special permissions listed above. Follow [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-sts-quickstart-guide) to manage users with an IDP.
+special permissions listed above. Follow [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/security-token-service.html) to manage users with an IDP.
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Client Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide)
-- [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-sts-quickstart-guide)
-- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO Client Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/security-token-service.html)
+- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/orchestration/README.md b/docs/orchestration/README.md
index d75402bc7..6b6d5cf3c 100644
--- a/docs/orchestration/README.md
+++ b/docs/orchestration/README.md
@@ -4,8 +4,7 @@ MinIO is a cloud-native application designed to scale in a sustainable manner in
| Orchestration platforms |
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
-| [`Kubernetes`](https://docs.min.io/docs/deploy-minio-on-kubernetes) |
-| [`Docker Compose`](https://docs.min.io/docs/deploy-minio-on-docker-compose) (only for test setups) |
+| [`Kubernetes`](https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/index.html#quickstart-for-kubernetes) |
## Why is MinIO cloud-native?
diff --git a/docs/orchestration/docker-compose/README.md b/docs/orchestration/docker-compose/README.md
index f93f35e63..38010a5ea 100644
--- a/docs/orchestration/docker-compose/README.md
+++ b/docs/orchestration/docker-compose/README.md
@@ -50,10 +50,10 @@ Distributed instances are now accessible on the host at ports 9000, proceed to a
* Update the command section in each service.
* Add a new MinIO server instance to the upstream directive in the Nginx configuration file.
- Read more about distributed MinIO [here](https://docs.min.io/docs/distributed-minio-quickstart-guide).
+ Read more about distributed MinIO [here](https://min.io/docs/minio/container/operations/install-deploy-manage/deploy-minio-single-node-multi-drive.html).
### Explore Further
* [Overview of Docker Compose](https://docs.docker.com/compose/overview/)
-* [MinIO Docker Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-docker-quickstart-guide)
-* [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide)
+* [MinIO Docker Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/container/index.html#quickstart-for-containers)
+* [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/container/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html)
diff --git a/docs/orchestration/kubernetes/README.md b/docs/orchestration/kubernetes/README.md
index d1698e478..7a46418e6 100644
--- a/docs/orchestration/kubernetes/README.md
+++ b/docs/orchestration/kubernetes/README.md
@@ -16,6 +16,6 @@ MinIO server exposes un-authenticated liveness endpoints so Kubernetes can nativ
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide)
+- [MinIO Erasure Code QuickStart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html)
- [Kubernetes Documentation](https://kubernetes.io/docs/home/)
- [Helm package manager for kubernetes](https://helm.sh/)
diff --git a/docs/select/README.md b/docs/select/README.md
index 98c6d21e4..ee5333d46 100644
--- a/docs/select/README.md
+++ b/docs/select/README.md
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ You can use the Select API to query objects with following features:
Type inference and automatic conversion of values is performed based on the context when the value is un-typed (such as when reading CSV data). If present, the CAST function overrides automatic conversion.
-The [mc sql](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide.html#sql) command can be used for executing queries using the command line.
+The [mc sql](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc/mc-sql.html) command can be used for executing queries using the command line.
(*) Parquet is disabled on the MinIO server by default. See below how to enable it.
@@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ To enable Parquet set the environment variable `MINIO_API_SELECT_PARQUET=on`.
### 1. Prerequisites
-- Install MinIO Server from [here](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
+- Install MinIO Server from [here](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#procedure).
- Familiarity with AWS S3 API.
- Familiarity with Python and installing dependencies.
@@ -113,12 +113,11 @@ For a more detailed SELECT SQL reference, please see [here](https://docs.aws.ama
## 5. Explore Further
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `mc sql` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-complete-guide.html#sql)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `mc sql` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc/mc-sql.html#command-mc.sql)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
## 6. Implementation Status
diff --git a/docs/shared-backend/README.md b/docs/shared-backend/README.md
index 8807befc0..843d78ba7 100644
--- a/docs/shared-backend/README.md
+++ b/docs/shared-backend/README.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ If you're aware of stand-alone MinIO set up, the installation and running remain
## 1. Prerequisites
-Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-quickstart-guide).
+Install MinIO - [MinIO Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html#quickstart-for-linux).
## 2. Run MinIO on Shared Backend
@@ -60,12 +60,11 @@ minio.exe gateway nas M:\export
## 3. Test your setup
-To test this setup, access the MinIO server via browser or [`mc`](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide). You’ll see the uploaded files are accessible from the all the MinIO shared backend endpoints.
+To test this setup, access the MinIO server via browser or [`mc`](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart). You’ll see the uploaded files are accessible from the all the MinIO shared backend endpoints.
## Explore Further
-- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/aws-cli-with-minio)
-- [Use `s3cmd` with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/s3cmd-with-minio)
-- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://docs.min.io/docs/golang-client-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [Use `mc` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html)
+- [Use `aws-cli` with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/integrations/aws-cli-with-minio.html)
+- [Use `minio-go` SDK with MinIO Server](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/go/minio-go.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/site-replication/README.md b/docs/site-replication/README.md
index 8fb7217bd..4d8f2cb50 100644
--- a/docs/site-replication/README.md
+++ b/docs/site-replication/README.md
@@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ The following Bucket features will **not be replicated**, is designed to differ
- All sites **must** have the same deployment credentials (i.e. `MINIO_ROOT_USER`, `MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD`).
- **Removing a site** is not allowed from a set of replicated sites once configured.
- All sites must be using the **same** external IDP(s) if any.
-- For [SSE-S3 or SSE-KMS encryption via KMS](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-kms-quickstart-guide.html "MinIO KMS Guide"), all sites **must** have access to a central KMS deployment. This can be achieved via a central KES server or multiple KES servers (say one per site) connected via a central KMS (Vault) server.
+- For [SSE-S3 or SSE-KMS encryption via KMS](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/server-side-encryption.html "MinIO KMS Guide"), all sites **must** have access to a central KMS deployment. This can be achieved via a central KES server or multiple KES servers (say one per site) connected via a central KMS (Vault) server.
## Configuring Site Replication
diff --git a/docs/sts/README.md b/docs/sts/README.md
index f814d88de..72aea5f2b 100644
--- a/docs/sts/README.md
+++ b/docs/sts/README.md
@@ -121,5 +121,5 @@ These credentials can now be used to perform MinIO API operations.
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/sts/assume-role.md b/docs/sts/assume-role.md
index 8d57480e8..e94b54103 100644
--- a/docs/sts/assume-role.md
+++ b/docs/sts/assume-role.md
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ export MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD=minio123
minio server ~/test
```
-Create new users following the multi-user guide [here](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-multi-user-quickstart-guide.html)
+Create new users following the multi-user guide [here](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/identity-access-management.html)
### Testing an example with awscli tool
@@ -134,5 +134,5 @@ SessionToken: eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJhY2Nlc3NLZXkiOiIyN1lEUllFT
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/sts/casdoor.md b/docs/sts/casdoor.md
index 786f350a4..d11814abe 100644
--- a/docs/sts/casdoor.md
+++ b/docs/sts/casdoor.md
@@ -112,5 +112,5 @@ This will open the login page of Casdoor, upon successful login, STS credentials
## Explore Further
- [Casdoor MinIO Integration](https://casdoor.org/docs/integration/minio)
-- [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-sts-quickstart-guide)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO STS Quickstart Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/developers/security-token-service.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/sts/client-grants.md b/docs/sts/client-grants.md
index ad5934458..1ae0286c9 100644
--- a/docs/sts/client-grants.md
+++ b/docs/sts/client-grants.md
@@ -111,5 +111,5 @@ $ go run client-grants.go -cid PoEgXP6uVO45IsENRngDXj5Au5Ya -csec eKsw6z8CtOJVBt
## Explore Further
-- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-admin-complete-guide.html)
-- [The MinIO documentation website](https://docs.min.io)
+- [MinIO Admin Complete Guide](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc-admin.html)
+- [The MinIO documentation website](https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html)
diff --git a/docs/sts/dex.md b/docs/sts/dex.md
index b0501fda9..507385861 100644
--- a/docs/sts/dex.md
+++ b/docs/sts/dex.md
@@ -99,5 +99,5 @@ and add relevant policies on MinIO using `mc admin policy add myminio/ :9000. Follow the below steps to connect to MinIO server with mc client:
- 1. Download the MinIO mc client - https://docs.minio.io/docs/minio-client-quickstart-guide
+ 1. Download the MinIO mc client - https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart
2. export MC_HOST_{{ template "minio.fullname" . }}-local=http://$(kubectl get secret {{ template "minio.secretName" . }} --namespace {{ .Release.Namespace }} -o jsonpath="{.data.rootUser}" | base64 --decode):$(kubectl get secret {{ template "minio.secretName" . }} -o jsonpath="{.data.rootPassword}" | base64 --decode)@:{{ .Values.service.port }}
3. mc ls {{ template "minio.fullname" . }}
-Alternately, you can use your browser or the MinIO SDK to access the server - https://docs.minio.io/categories/17
+Alternately, you can use your browser or the MinIO SDK to access the server - https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-server/minio-server.html
{{- end }}
{{ if and (.Values.networkPolicy.enabled) (not .Values.networkPolicy.allowExternal) }}
diff --git a/helm/minio/values.yaml b/helm/minio/values.yaml
index 865edf02b..dd048d40e 100644
--- a/helm/minio/values.yaml
+++ b/helm/minio/values.yaml
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ runtimeClassName: ""
## Set default rootUser, rootPassword
## AccessKey and secretKey is generated when not set
-## Distributed MinIO ref: https://docs.minio.io/docs/distributed-minio-quickstart-guide
+## Distributed MinIO ref: https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/install-deploy-manage/deploy-minio-multi-node-multi-drive.html
##
rootUser: ""
rootPassword: ""
@@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ tls:
publicCrt: public.crt
privateKey: private.key
-## Trusted Certificates Settings for MinIO. Ref: https://docs.minio.io/docs/how-to-secure-access-to-minio-server-with-tls#install-certificates-from-third-party-cas
+## Trusted Certificates Settings for MinIO. Ref: https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/network-encryption.html#third-party-certificate-authorities
## Bundle multiple trusted certificates into one secret and pass that here. Ref: https://github.com/minio/minio/tree/master/docs/tls/kubernetes#2-create-kubernetes-secret
## When using self-signed certificates, remember to include MinIO's own certificate in the bundle with key public.crt.
## If certSecret is left empty and tls is enabled, this chart installs the public certificate from .Values.tls.certSecret.
@@ -341,7 +341,7 @@ makePolicyJob:
users:
## Username, password and policy to be assigned to the user
## Default policies are [readonly|readwrite|writeonly|consoleAdmin|diagnostics]
- ## Add new policies as explained here https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-multi-user-quickstart-guide.html
+ ## Add new policies as explained here https://min.io/docs/minio/kubernetes/upstream/administration/identity-access-management.html#access-management
## NOTE: this will fail if LDAP is enabled in your MinIO deployment
## make sure to disable this if you are using LDAP.
- accessKey: console
@@ -444,7 +444,7 @@ customCommandJob:
## Use this field to add environment variables relevant to MinIO server. These fields will be passed on to MinIO container(s)
## when Chart is deployed
environment:
- ## Please refer for comprehensive list https://docs.min.io/minio/baremetal/reference/minio-server/minio-server.html
+ ## Please refer for comprehensive list https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-server/minio-server.html
## MINIO_SUBNET_LICENSE: "License key obtained from https://subnet.min.io"
## MINIO_BROWSER: "off"
@@ -456,7 +456,7 @@ environment:
## OpenID Identity Management
## The following section documents environment variables for enabling external identity management using an OpenID Connect (OIDC)-compatible provider.
-## See https://docs.min.io/minio/baremetal/security/openid-external-identity-management/external-authentication-with-openid-identity-provider.html#minio-external-identity-management-openid for a tutorial on using these variables.
+## See https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/external-iam/configure-openid-external-identity-management.html for a tutorial on using these variables.
oidc:
enabled: false
configUrl: "https://identity-provider-url/.well-known/openid-configuration"
diff --git a/internal/config/errors.go b/internal/config/errors.go
index c675da76c..83802a825 100644
--- a/internal/config/errors.go
+++ b/internal/config/errors.go
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ var (
ErrInvalidCacheEncryptionKey = newErrFn(
"Invalid cache encryption master key value",
"Please check the passed value",
- "MINIO_CACHE_ENCRYPTION_SECRET_KEY: For more information, please refer to https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-disk-cache-guide",
+ "MINIO_CACHE_ENCRYPTION_SECRET_KEY: For more information, please refer to https://blog.min.io/deprecation-of-the-minio-gateway/",
)
ErrInvalidCacheRange = newErrFn(
@@ -172,13 +172,13 @@ var (
ErrInvalidErasureEndpoints = newErrFn(
"Invalid endpoint(s) in erasure mode",
"Please provide correct combination of local/remote paths",
- "For more information, please refer to https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide",
+ "For more information, please refer to https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html",
)
ErrInvalidNumberOfErasureEndpoints = newErrFn(
"Invalid total number of endpoints for erasure mode",
"Please provide number of endpoints greater or equal to 2",
- "For more information, please refer to https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-erasure-code-quickstart-guide",
+ "For more information, please refer to https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/concepts/erasure-coding.html",
)
ErrStorageClassValue = newErrFn(
@@ -257,7 +257,7 @@ Example 1:
ErrNoCertsAndHTTPSEndpoints = newErrFn(
"HTTPS specified in endpoints, but no TLS certificate is found on the local machine",
"Please add TLS certificate or use HTTP endpoints only",
- "Refer to https://docs.min.io/docs/how-to-secure-access-to-minio-server-with-tls for information about how to load a TLS certificate in your server",
+ "Refer to https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/operations/network-encryption.html for information about how to load a TLS certificate in your server",
)
ErrCertsAndHTTPEndpoints = newErrFn(
@@ -293,7 +293,7 @@ Example 1:
ErrInvalidGWSSEEnvValue = newErrFn(
"Invalid gateway SSE configuration",
"",
- "Refer to https://docs.min.io/docs/minio-kms-quickstart-guide.html for setting up SSE",
+ "Refer to https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/administration/server-side-encryption/server-side-encryption-sse-kms.html#quickstart for setting up SSE",
)
ErrInvalidReplicationWorkersValue = newErrFn(